Intro: Incredible India an organisation started in the year is an international marketing campaign by the Government of India to promote tourism in India to a global audience. The title was officially branded and promoted by Amitabh Kant, the former Secretary under the Ministry of tourism. This land is your land; This land is my land; Jun 02, · Essay on Incredible India 91 Chapter 5 Sources of plant nutrients and soil amendments A large number of diverse materials can serve as sources of Dec 11, · Tourism is a major industry in India and the Ministry of Tourism launched a campaign to promote Incredible India as a tourist destination in [2] The phrase “Incredible India” was adopted as a slogan by the ministry. Before , the Indian government regularly formulated policies and prepared pamphlets and brochures for the promotion of tourism, Estimated Reading Time: 4 mins
Incredible India Essay Example | GraduateWay
These can be natural, synthetic, recycled wastes or a range of biological products including microbial inoculants. Except for microbial inoculants biofertilizersall of these contain one, two or several plant nutrients in readily or potentially available forms. A certain supply of mineral and organic nutrient sources is present in soils, but these often have to be supplemented with external applications for better plant growth. In practical farming, a vast variety of sources can find use in spite of large differences in their nature, nutrient contents, forms, physicochemical properties and rate of nutrient release. These are not mutually exclusive but can be used together as components of INM. Nutrient sources are generally classified as organic, mineral or biological.
Organic nutrient sources are often described as manures, bulky organic manures or Organic fertilizers. Most organic nutrient sources, including waste materials, have widely varying composition and often only a low concentration of nutrients, which differ in their availability. Some of these, such as cereal straw, release nutrients only slowly owing to a wide C:N ratio while others such as the N-rich leguminous green manures or oilcakes decompose rapidly and release nutrients quickly. Residues from processed products of plant or animal origin are increasingly important as nutrient sources and lead to nutrient saving by recycling. In addition, a very wide range of products obtained from the recycling of crop, animal, human and industrial wastes can and do serve as sources of plant nutrient.
Order custom essay Incredible India with free plagiarism report. A significant amount of N is made available through BNF by a number of micro-organisms in soils either independently or in symbiosis with certain plants. The inocula of such micro-organisms are commonly referred to as biofertilizers, which are used to enhance the N supply for crops. The majority of nutrient input to agriculture comes from commercial mineral fertilizers. Organic manures are considered to play a significant but lesser role in nutrient contribution, leaving aside their beneficial effects on soil physico-chemical and biological properties.
Such a conclusion could be due in part to inadequate data on the production and consumption of organic sources as compared with mineral fertilizers. Appreciable amounts of nutrients can also be brought in with rain e. atmospheric deposition of nitrate and sulphate and with irrigation water. This chapter describes common sources of plant nutrients. Incredible india essay last section deals with various soil amendments. Chapters 7 and 8 provide guidelines for the application of various nutrients through different sources. Definition, classification and general aspects Definition The term fertilizer is derived from the Latin word fertilis, which means fruit bearing.
Fertilizer can be defined as a mined, refined or manufactured product containing one or more essential plant nutrients in available or potentially available forms and in commercially valuable amounts without carrying any harmful substance above permissible limits, incredible india essay. Many prefixes such as synthetic, mineral, incredible india essay, inorganic, artificial or chemical are often used to describe fertilizers and these are used interchangeably. Although organic fertilizers are also being prepared and used, they are not yet covered by the term fertilizers, largely owing to tradition and their generally much lower nutrient content.
Strictly speaking, the most common mineral fertilizer, urea, is an organic compound that releases plant available N after transformation in the soil. In this section, the term fertilizer is used in a more narrow sense and widest acceptability. Fertilizer grade is an expression used in extension and the fertilizer trade referring to the legal guarantee of the available plant nutrients expressed as a percentage by weight in a fertilizer, e. a 12—32—16 grade of NPK complex fertilizer indicates the presence of 12 percent nitrogen Nincredible india essay, 32 percent phosphorous pentoxide P2O5 and 16 percent potash K2O in it.
On a fertilizer bag, the NPK content is always written in the sequence N, P2O5 and K2O, incredible india essay. Synthetic fertilizers are sometimes referred to as being artificial or chemical fertilizers, implying that these are inferior to those termed natural mainly organic products. However, fertilizers are neither unnatural nor inferior products. Many fertilizers are finished products derived from natural deposits, either made more useful for plants e. phosphate fertilizer or separated from useless or even harmful components e. K fertilizer. Although most N fertilizers are indeed produced artificially, i, incredible india essay. synthesized in chemical factories, their N is derived from atmospheric air and their components such as nitrate, ammonia or urea are identical with the substances normally occurring in soils and plants.
The primary source of all P in fertilizers is PR, a natural mineral that has to be mined, refined and solubilized in order to be useful. Fertilizers have been traditionally classified as follows:? Straight fertilizers: These contain one of the three major nutrients N, P or K. This is a traditional term referring to fertilizers that contain and are used for one major nutrient as opposed to multinutrient fertilizers. For secondary nutrients, these incredible india essay products containing elemental S, magnesium sulphate, calcium oxide, etc. In the case of micronutrients, incredible india essay, borax, Zn and Fe chelates and sulphate salts of micronutrients are straight fertilizers. However, the term is not often used for micronutrient carriers.
This is not a very accurate term because many straight fertilizers also contain other essential plant nutrients, such as S in ammonium sulphate. These can also be termed single-nutrient Chapter 5 — Sources of plant nutrients and soil amendments 93 fertilizers. The term focuses on the most important nutrient for which a product was traditionally used disregarding other valuable constituents. In a strict sense, incredible india essay, the term is justified only for products such as urea, ammonium nitrate ANand elemental S. They are produced by incredible india essay chemical reaction between the raw materials containing the desired nutrients and they are generally solid granulated products.
These include both two-nutrient NP and threenutrient NPK fertilizers. These are also referred to as multinutrient fertilizers, but do not incredible india essay fertilizer mixture or bulk blends as no chemical reaction is involved. Incredible india essay term is rarely used for multimicronutrient fertilizers or fortified fertilizers containing both macronutrients and micronutrients or for liquid fertilizers. The term multinutrient fertilizers is more appropriate as it includes both major nutrients and micronutrients.
Moreover, it does not restrict itself to a particular production process. A brief historical overview The use of fertilizers started in the early nineteenth century when saltpetre and guano where shipped from Chile and Peru to the United Kingdom and Western Europe, respectively. Production of potash fertilizers started in in Germany and of that N fertilizers incredible india essay ammonia derived from coal in about A significant advance in the production technology of N fertilizers came with the production of synthetic ammonia by incredible india essay Haber-Bosch process in Germany in Production and use of urea as a fertilizer started from Since then, a large variety of solid and liquid fertilizers containing one, two or several plant nutrients have been produced and used.
The fertilizer scene is dominated by products containing N, P and K in many chemical and physical forms and their combinations in order to meet the need for their application under different conditions throughout the world. General aspects In most countries, the effectiveness and safe use of substances to be registered as fertilizers is ensured by law. Recently, in developed countries, there has been a trend towards regulating some aspects of fertilizer application in respect of pollution. The nutrient concentration incredible india essay fertilizers is traditionally expressed in terms of N, P2O5, K2O, etc. For example, an NPK fertilizer 15—15—15 contains 15 percent each of N, incredible india essay, P2O5 and K2O, or 45 percent total nutrients.
The percentage composition of a fertilizer refers mostly to the total concentration of a nutrient, but sometimes only to its available portion. For solid fertilizers, the percentage generally refers to the weight basis, e. For 94 Plant nutrition for food security liquid fertilizers, both weight and incredible india essay percentages are used, e. In scientific literature, incredible india essay, the nutrients are expressed mostly in elemental form whereas the industry, trade and extension services continue to express P and K in their oxide forms.
The fact is that neither N nor P exists in soils, plants or fertilizers in elemental form. In any case, incredible india essay, owing to the mismatch between the forms in which plant nutrients are expressed in research, extension and trade literature, care is needed when converting research data into incredible india essay values. From small beginnings in the nineteenth century, the use of fertilizers has grown dramatically. Five countries China, the United States of America, India, Brazil and France account for 61 percent of the total fertilizer consumption, while more than half of total consumption takes place incredible india essay China, the United States of America and India, incredible india essay. The nutrient consumption rate in different countries varies from very high to extremely low Figure 2, incredible india essay.
Even more than years after the beginning of fertilizer use, incredible india essay, there are still large areas of the world where no or very little fertilizer is used. Fertilizers containing nitrogen Origin All N in fertilizers originates from the nitrogen gas N2 in the atmosphere, which contains 79 percent N by volume. Above every hectare of land at sea level, there are 78 tonnes of N2. This is the N that is converted into ammonia in the fertilizer factories, and this is also the N that is fixed biologically into ammonium by various micro-organisms. Thus, there are abundant supplies of N for the production of nitrogenous fertilizers. Only a small amount of fertilizer N is still obtained from natural deposits such as Chile saltpetre and guano.
Chapter 5 — Sources of plant nutrients and soil amendments 95 N is captured from the air, N fertilizer production is incredible india essay a matter of available energy, incredible india essay, which is mainly derived from oil or natural gas reserves. Production of N fertilizers The main features of the production of N fertilizers are:? Ammonia: It is the starting point and basic intermediate for the production of N fertilizers. It is synthesized by the Haber-Bosch reaction which combines the very stable molecule of atmospheric N2 with hydrogen, e. Nitrate fertilizers: In this case, nitric acid HNO3 is produced by the oxidation of ammonia and then neutralized with materials such as calcium carbonate CaCO3 to produce calcium nitrate Ca NO3 2.
Nitrate fertilizers may also be derived from other sources such as Chile saltpetre. Ammonium nitrate AN fertilizers: These are produced by neutralizing nitric acid derived from the oxidation of ammonia with ammonia. The solid granulated fertilizer is obtained by spraying the highly concentrated solution in cooling towers. AN with lime: It is produced: i by mixing AN with calcium carbonate to obtain calcium ammonium nitrate CAN ; and ii by the reaction of calcium nitrate with ammonia and CO2. Urea: It is produced by the reaction of NH3 and CO2 at atmospheric pressure and a temperature of °C. Care is needed during drying to ensure that the biuret formed is minimum and within the permissible limits set out in fertilizer-quality standards. Consumption of N fertilizers The annual consumption of N through fertilizers is almost 85 million tonnes of N —03 data.
Out of this total, more than 50 million tonnes of N is consumed in five countries China, United States of America, India, France and Brazil. China, India and the United States of America each consume more than 10 million tonnes of N through fertilizers annually. The number of N-containing fertilizers is large. Straight Incredible india essay fertilizers are listed in Table 16 and the major ones are described below. Multinutrient fertilizers containing N are discussed in a later section. Anhydrous ammonia Gaseous ammonia can be used directly as a fertilizer. It has a pungent odour and is toxic to plants and humans when concentrated but harmless in dilute form.
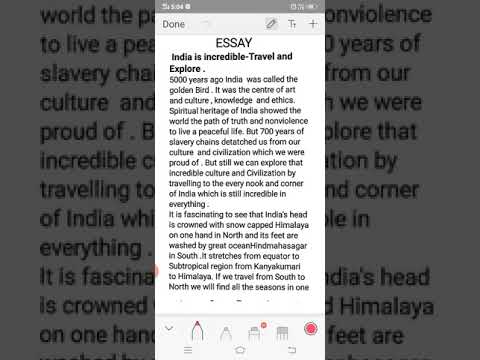
Essay on India is Incredible Travel and Explore - Essay Writing India is Incredible Travel Explore
, time: 2:20Incredible India - blogger.com

At almost every door step, one will see the ‘Swastik’ (a holy cross), a symbol of Lord Ganesha, the God of good beginnings. Alongside, there will be the sacred words ‘shubh’ and ‘labh’, which are the names of Lord Ganesha’s sons. This is a notion to please Lord Ganesha and Goddess Lakshmi, who are believed to bring prosperity Apr 11, · Essay on Incredible India: India is a country wherever individuals speak several languages and other people of various castes, creeds, religions, and cultures live along. That’s why India is legendary for the commonly spoken language of “unity in diversity”. It’s well known because of the land of spirituality, philosophy, science, and technology. Individuals of varied Essay on Incredible India ‘Atithi Devo Bhava’ - the most famous saying means guests are like God and it is the spirit of the Indian tradition and culture when they welcome their guests. It truly reflects the rich and cultural heritage and warm hospitality of the people of blogger.comted Reading Time: 7 mins
No comments:
Post a Comment